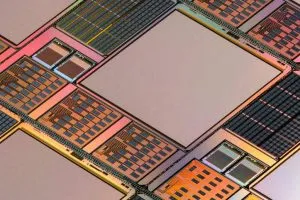
This is the world’s first x-ray image sensor to directly convert radiation into electronic signals using quantum dots on a CMOS IC, according to Swiss innovation center CSEM, which made it with Dutch nano particle start-up QDI Systems. The IC is a custom transistor array sensitive to carriers released by the coating. Designed to be spray-applied, the active parts of ...
Nano-Imprint
Nano-imprint lithography is an emerging technology that enables high-resolution patterning of nanostructures in semiconductors, optical devices, and biomaterials. Recent innovations in nano-imprint techniques are pushing the boundaries of miniaturization in electronics manufacturing, enabling cost-effective mass production of nano-scale components. As industries demand higher precision and lower costs, nano-imprint technology offers an efficient alternative to traditional photolithography for semiconductor production. With applications in displays, sensors, and quantum computing, nano-imprint is paving the way for the next generation of electronics devices and pushing the limits of microelectronics innovation.
Tiny inductor-inclusive nano-power dc-dc IC
Torex Semiconductor has created a nano-power dc-dc converter that can occupy only 7.7 x 3.1mm with all external capacitors – the necessary inductor is inside the device package. Called XCL108 and drawing 400nA quiescent current, it is a boost converter that will operate from inputs between 650mV and 5.5V – starting from anything above 1.6V. The device is a series, ...
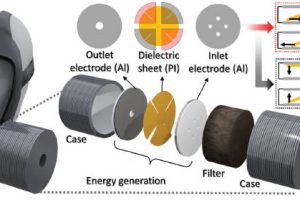
Modern twist on clockwork stores more energy
Forget exploiting carbon nanotubes electrochemically, and just wind them up like clockwork if you want to store energy. This is not quite the message that researchers at the University of Maryland Baltimore County are delivering, but it might as well be as a team from there is storing 2.1MJ/kg in twisted carbon nanotubes – more, weight-for-weight, than Li-ion chemistry can ...
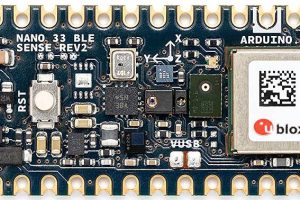
Arduino swaps sensors on Nano 33 BLE and Nano 33 BLE Sense
Arduino has bought out second revisions of its Nano 33 BLE and Nano 33 BLE Sense bluetooth-equipped microcontroller boards, keeping the sensor mix, but changing several of the sensor ICs. The nRF52840 IC (via a u-blox NINA-B306 module) stays the same, and still provides both an Arm Cortex-M4 processor and a Bluetooth transceiver – to go with these is an ...
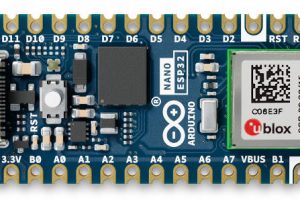
Arduino puts Wi-Fi and Bluetooth ESP32 processor into Nano
Arduino has introduced a Nano shaped board with a Wi-Fi and Bluetooth LE capable Espressif’s ESP32-S3 microcontroller, supporting it with the Arduino IDE and MicroPython. “Beginners can explore in an easy-to-understand, welcoming environment, with a popular MCU supported by documentation and a global community of users,” said Arduino. “At the same time, more advanced users can take advantage of the ...
CES: Bosch senses turn rate, acceleration, magnetism, pressure and particulates
Bosch Sensortec announced four sensors all on the same day at CES in Las Vegas. BMP585 (right) is a toughened liquid-resistant barometer for altitude tracking in wearables. With a liquid-proof gel cover, it can be exposed to salt water and chlorinated swimming pool water – as well as dust, for example as part of a vacuum cleaner. “It includes all the ...
Breath-powered Bluetooth for gas masks
Researchers from Chung-Ang University in Korea have developed a harvester that collects energy from breath in a gas mask, and have used it to power a harmful gas sensor. The harvester is a form of teng (tribo-electric nano-generator, explained at the bottom here) that use motion and electric charge to cause an ac current in an external circuit. This one ...
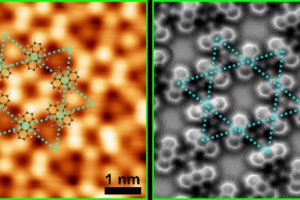
Non-magnetic 2-d materials yield designer magnetic properties for spintronics
Scientists in Australia have opened the door to self-assembling controllable nano-scale electronic and spintronic devices by discovering how magnetism arises in 2-d ‘kagome’ metal-organic frameworks. Kagome materials have repeating pattern of hexagons and smaller triangles, with the hexagons touching at their tips (images below). The word is Japanese, relating to a basket weaving pattern. In this case, the metal-organic is ...
A simpler source of THz radiation
Plasmon-coupled semiconductor surface states can down-convert 1550nm optical wavelengths to terahertz frequencies four-orders of magnitude more efficiently than non-linear optical methods, according to UCLA. When a crystal is a semiconductor – p-doped InAs in this case – the ‘surface states’ created by the left-over bonds that are inevitable on the outside of a crystal lattice can create high gradient electric ...
‘Microchip Technology Caldicot’ in Wales works on nano-relay logic project
Microchip has changed the name of its UK subsidiary that is working on nano-relay-based logic and memory for an EU ultra-low-power computing and memory project. Caldicot-based Microsemi Semiconductor is now ‘Microchip Technology Caldicot’. “The organisation is the lead partner in the ZeroAMP Project, an industry-driven initiative funded by the Horizon2020 EU Research and Innovation Program that is focused on developing ...
 Electronics Weekly
Electronics Weekly