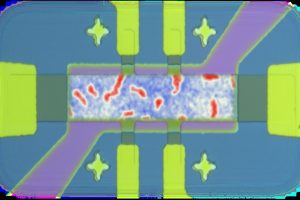
Researchers from the University of Southampton have found a way to make an optically-active meta-surface without altering the physical shape of the surface. Infra-red thermal control coatings and non-linear optics are potential applications. Metasurfaces are structures designed to control, for example, electromagnetic radiation using repeating structures, typically with sub-micrometer dimensions for light. Routes to forming these structures include etching away ...
Research
The latest electronics research news from within the industry and universities from around the world.
Rohm starts lab in China for automotive power electronics
Japanese power component supplier Rohm has teamed up with Chinese electric power train company Leadrive Technology to build a joint silicon carbide power laboratory in the Shanghai free trade zone. The two companies have been collaborating since 2017, when Leadrive was established. “Establishing a joint research lab centred on vehicle power modules and inverters utilising Rohm’s SiC mosfet bare chips ...
Commercial AI is likely to cheat you, unless trained not to
Artificial intelligence that tricks you into paying more for things has come under the academic spotlight in a project by Swiss lab EPFL and British partners. The research found that, unless specifically checked, AI can easily resort to manipulative strategies. It also identified drivers towards these unethical practices, and ways to design them out of AI training algorithms. EPFL statistician ...
A step on the road to skyrmion memories
US researchers have manipulated fixed magnetic skyrmions using voltages, offering a possible route to skyrmion memory. Magnetic skyrmions are self-contained stable spin fields that share some characteristics with particles. They can be only a few nanometres across, and in certain circumstances can be created, destroyed and manipulated with very little energy, leading to them being studied as a possible memory ...
Self-hollowing nano-particles store lithium for batteries
Spontaneously-hollowing antimony particles could increase the capacity of lithium ion cells, according to the Georgia Institute of Technology. “Intentionally engineering hollow nano-materials has been done for a while now, and it is a promising approach for improving the lifetime and stability of batteries with high energy density,” GaTech research engineer Matthew McDowell. “The problem has been that directly synthesising these ...
Royal Society takes its Summer Science Exhibition online
This year, in the wake of Covid-19, the Royal Society’s Summer Science Exhibition is going online. Running from 13 – 17 July, the free event aims to celebrate advances in science and scientific research. It features a week of interactive quizzes, creative challenges and a range of talks on science topics, including the science of pets, doping in sports and ...
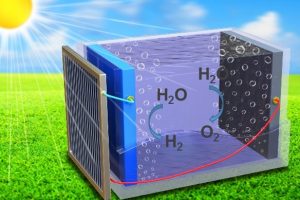
Perovskite solar pushes up efficiency in hydrogen-making cell
Scientists in Australia have used a custom perovskite solar cell to increase the efficiency of solar hydrogen production close to the point thought to be commercially viable. Solar-to-hydrogen production from water and light was 17.6% efficient, despite the relatively humble solar materials involved – silicon and perovskite – compared to a 20% target set by the US Department of Energy ...
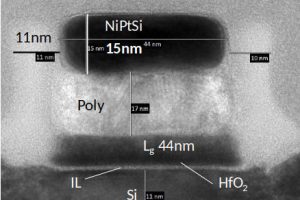
Leti makes CMOS at 500°C for 3D sequential chips
CEA-Leti scientists have made FDSOI CMOS at 500°C, “while showing strong performance gains especially in p-type MOS logic devices”, according to the French lab, which has branded the process ‘CoolCube’. 500°C processing is important when trying to shrink die by building CMOS with p-channel mosfets above rather than next to their n-channel counterparts – called a ‘3D sequential’ structure. If too much ...
A new approach to skin chemistry sensing
Engineers at University of California Los Angeles have found a way to create a stretchable adhesive skin chemistry sensor without serpentine electrical conductors. Instead, they persuaded the liquid sweat to pipe itself sideways through a flexible film layer between electrodes – maintaining stretchability – while electrical connections are made through the thickness of the sensor to a rigid electrode array at the ...
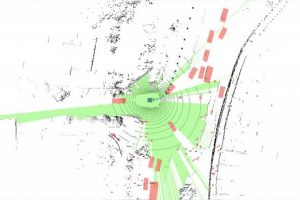
To improve self-driving algorithms, add the concept of empty space
Teaching self-driving artificial intelligence about the empty space around it could improve the recognition of surrounding objects, according to researchers at Carnegie Mellon University – combining the merit of classic mapping and deep learning for 3D object detection. According to the university, when tested against a standard benchmark, the new method outperformed the previous top-performing technique – improving detection by ...
 Electronics Weekly
Electronics Weekly